INTRODUCTION
Colon and rectum cancer is cancer that attacks the colon and rectum .Disease is a deadly cancer ranks second.The colon is part of the digestive system .As we know the digestive system starts from the mouth, and throat (esophagus), stomach , small intestine (duodenum, yeyunum, ileum), large intestine (colon), rectum and ends at the rectum .The large intestine consists of colon and rectum. Colon or large intestine is the colon after the small intestine, consisting of the right colon (ascending colon), colon next to the middle of the top (transverse colon) and left colon (descending colon).After the colon, rectum which is then above the anal channel.Part of the colon associated with the small intestine called the caecum, while the colon is associated with the rectum called the sigmoid colon.
Cancer is a disease of the growth of cells that are malignant.Can the organ in the body of any human being .When attacked in the colon, it is called colon cancer, when the on the rectum, it is called rectal cancer. When the colon or rectum is called colorectal cancer.
Colon cancer as other cancer properties, has properties can grow relatively quickly, can infiltrate or root (infiltration) into the surrounding tissue and destroying it, can be spread further through the lymph nodes and blood vessels to distant organs grown from its original location, such as the liver , the lungs , which can eventually cause death if not treated properly.
Many factors can increase the risk of rectal cancer, including a high-fat diet, low in fiber, more than 50 years of age, suffered a personal history of colorectal adenoma or adenocarcinoma had a higher risk of 3-fold, a level-generation family history with a history of colorectal cancer have a risk 3-fold greater, Familial polyposis coli, Gardner syndrome, and Turcot syndrome, in all these patients without colectomy performed can develop into a slightly increased risk of rectal cancer in patients with juvenile polyposis syndrome, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, and Muir syndrome. Occurs in 50% of patients with Hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer Inflammatory bowel disease

Clinical signs and symptoms that may appear on rectal cancer is a change in bowel habits adnya blood in the stool, either fresh or utu dareah black, diarrhea, konstipasu or feel that the content of the stomach is not completely empty the stool, smaller stool than usual, complaints such as stomach discomfort often flatus, bloating, feeling of fullness in the abdomen or pain. Weight loss is not known why, nausea and vomiting, feeling tired and lethargic.
The division of stages based on the Duke's classification system.The tests are complete blood tests, digital rectal, barium enema, sigmoidoscopy, colonoscopy.
Therapy consisted of curative and palliative therapy. Curative treatment is with surgery. Palliative therapy with chemotherapy and radiation.
SECTION II
Anatomy and Physiology
The anal canal is derived from an invagination proktoderm ectoderm, whereas the rectum comes from the entoderm. Because of differences in the anus and rectum is bleeding, neurological, and penyaliran limfnya different vein and also, as well as the epithelial covering. The rectum is lined by intestinal mucosa glanduler while the anal canal by anoderm which is an advanced squamous epithelium coated outer shell.
No one called the anal mucosa. Boundary regions of the rectum and anal canal is marked by changes in the epithelial type. Anal canal and the outer skin and the surrounding somatic sensory innervation is rich and sensitive to pain stimuli, while the rectal mucosa has persrafan autonomic and insensitive to pain. Pain is not a person with early symptoms of carcinoma of the rectum, anal fissure pain was temporary.
Above the venous blood flow through the sis tem anorektum port, while derived from the anus to the system dialrkan v.iliaka cava through a branch. This distribution is important in understanding how the spread of malignancy and infection as well as the formation of hemorrhoids.Limf system drain its contents from the rectum through the vessels along the vascular hemoroidalis limf superior to the lymph nodes limf paraaorta through the internal iliac gland, whereas limf derived from the anal canal flowing into the inguinal glands.
Anal canal length measuring approximately 3 inches. Ventrokranial axis leads to the umbilicus toward a real and an angle to the dorsal to the rectum in a resting state. At the time of defecation angle becomes larger.Upper limit of the anal canal is called the line anorektum, mucocutaneous line, linea pektinata or dentate line. In this area there kripta anus and anal glands of the mouth between the columns of the rectum. Infections that occur here can cause abscesses that can form a fistula anorektum. Inter-circular indentation sphincter can be palpated in the anal canal when performing digital rectal, and shows the boundary between the internal sphincter and external sphincter (Hilton line)
Lanalis ring encircling the anal sphincter consists of analysts and the internal sphincter and external sphincter. Posterior and lateral sides of the ring is formed from the fusion of the internal sphincter, longitudinal muscle, the central part of the levator muscle (puborektalis), and components of the external m.sfingter. M.sfingter internus consisted of smooth muscle fibers, whereas the external m.sfingter composed of striated muscle fibers.
Arterial bleeding
Hemoroidalis superior artery is a direct continuation a.mesenterika inferior.The artery divides into two main branches: the left and right. The right branch forked again. The location of the last three branches may be able to explain where the typical is hemorrhoids in two pieces in each quarter to the right and a left lateral quarter.
Artery is a branch of the anterior medial hemoroidalis a.iliaka internal, while the inferior is a.hemoroidalis a.pudenda internal branch. Anastomosis between the inferior and superior vascular arcade is a collateral circulation which has important significance in the follow-surgical or atherosclerotic blockages in the aorta and branching a.iliaka. The collateral vascular anastomosis to the inferior hemorrhoidal bleeding can menjmin in both lower extremities. Hemoroidalis plexus bleeding in the vast and rich collateral blood so that bleeding from internal hemorrhoids produce fresh red blood and venous blood instead of bluish color.
Venous bleeding
Venous plexus derived from the superior hemoroidalis hemoroidalis internus and walked toward the cranial to the v. and so on through the inferior mesenteric vein v.lienalis to. These veins are not berkatup abdominal cavity so that the pressure determines the pressure in it. Rectal carcinoma can spread as a venous embolus to the heart, while the septic embolus can lead to pileflebitis. V.hemoroidalis inferior blood to the internal and v.pudenda v.iliaka into the system of internal and kava. Enlargement v.hemoroidalis dpat cause hemorrhoidal complaints.
Penyaliran limf
Lymph vessels form a plexus of fine canal menyalirkan contents to the inguinal lymph nodes, then from here limf fluid continues to flow to the iliac lymph nodes. Infections and malignant tumors in the anal area can cause inguinal lymphadenopathy. Limf vessels of the rectum at the top of the line anorektum go hand in hand with superior v.hemoroidalis and continue to the inferior mesenteric lymph nodes and aorta. Radical surgery for carcinoma of the rectum and anus eradiksi based on the anatomy of this limf channel.
Innervation
The nerves of the rectum consists of the sympathetic system and the parasympathetic system. Sympathetic fibers from the inferior mesenteric plexus and of the system formed parasakral lumbar sympathetic ganglion of the second segment, third, and fourth.Elements of the sympathetic plexus toward the genital structures and smooth muscle fibers that control the emission of semen ejaculated. Parasympathetic innervation (spiral erigentes) derived from the second sacral nerve, third, and fourth. These nerve fibers leading to the erectile tissue of the penis and clitoris as well as control the erection by regulating the flow of blood into the tissues.Therefore, nerve injury that occurred at the stage of radical surgery such as the rectum or uterus ekstirpasi redikal, vesicles can cause urinary dysfunction and sexual dysfunction.
Muscular puborektal mempertahnkan anorektum angle; muscle is to sharpen the point when the stretch and straighten the intestine when the slack.
Continence
Anal continence depends on faecal continence, pressure inside the anus, the pressure in the rectum, and anorectal angle. The more watery stools, more and more difficult to keep him in the gut. Pressure at rest in the atmosphere ranged between 25-100 mmHg anus and in the rectum between 5-20 mmHg. If the angle between the rectum and anus more than 80 degrees, the hard stool is maintained.
Defecation
In the normal atmosphere, the rectum is empty. Removal of stool from the rectum into the sigmoid colon is sometimes triggered by eating, especially in infants. If the contents of the sigmoid into the rectum, felt by the rectum and cause a desire to defecate. The rectum has a unique ability to recognize and separate the solids, liquids, and gases.
Posture during defecation, which is sitting or squatting position, plays a mean. Defecation caused by rectal peristalsis reflex, assisted by straining and relaxation of the external anal sphincter.
Requirement for normal defecation innervation is sensible for the content of rectal sensation and anal sphincter innervation to a complete contraction and relaxation, peristalsis of the colon and rectum are not disturbed, and the anatomical structure of the pelvic organs are intact.
Absolute requirement for normal defecation
Almost all of the disorders or diseases of the anorektum diagnosis can be made based on history and physical examination including inspection and palpation of the area perianus and digital examination, anoscopy examination, and examination proktisigmoidoskopi.
Figure 1. Anatomy of the colon and rectum
SECTION III
CARCINOMA rectum and colon
III.1 EPIDEMIOLOGY
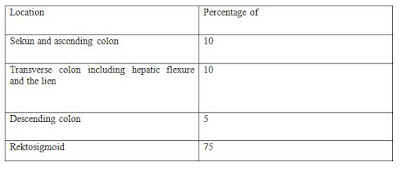
Colon and rectum cancer is cancer that attacks the colon and rectum. This disease is a cancer of the deadly pertingkat to 2. The colon is part of the digestive system, consisting of the colon and rectum. Colon or large intestine consists of the right colon (ascending colon), colon next to the middle (transverse colon), the right colon (colon descenden).After the colon before the rectum which is the channel on the anal. Part of the colon associated with the small intestine called the caecum, while the colon is associated with the rectum called the sigmoid colon. The incidence of carcinoma of the colon and rektun in Indonesia is quite high, as well as mortality.Comparable incidence in men and women, and more on young people. About 75% are found in rektosigmoid. In western countries comparison of male and female = 3:1, less than 50% was found in rektosigmoid, and is a disease of elderly people. Digital rectal examination is a determinant of rectal carcinoma.
III.2 Etiology
Until now not known with certainty what penyeban colorectal cancer. Artifacts are some risk factors that cause a person to be susceptible to colorectal cancer are:
• Age, colorectal cancer is generally attacked more frequently in old age.More than 90 percent of the disease have occurred in patients over the age of 50 years. Although at a younger age than 50 tahunpun can be affected. Approximately 3% of cancer patients are attacked at the age below 40 years.
• Polyps Colorectal, is the growth of tumor in the inner wall of the colon and rectum.Often occurs in over 50 years. Most polyps are benign, but some can turn into cancer. Find and remove these polyps can reduce the risk of colorectal cancer.
• Family history of colorectal cancer, if the affected family (parents, brother, sister or child), then the risk for this cancer becomes larger, especially when families are affected by esophageal cancer at a young age.
• Genetic disorders, changes in certain genes increase the risk of colorectal cancer.The most frequent form of gene abnormalities that can cause hereditary nonpolyposis cancer is colon cancer (HNPCC), caused a change in the HNPCC gene.About three out of four patients with HNPCC gene defect will develop colorectal cancer, where the most common age at diagnosis is over the age of 44 years.
• Had suffered from similar diseases, may be attacked again by the same disease a second time.Similarly, women who have a history of ovarian cancer, uterine cancer, breast cancer has a high risk for this cancer.
• Colitis, ulcerative colitis or a form of Crohn disease that causes inflammation or inflammation of the intestine for a long time, will increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
• Diet , foods high in fat (especially animal fat ) and low calcium , low folate and fiber, rarely eat vegetables and fruits, drinking alcohol, will increase the risk of colorectal cancer.
• Smoking, may increase the risk of this cancer.
III.3 LAYOUT
Approximately 70-75% of colon and rectal carcinoma located in the rectum and sigmoid. This situation is in accordance with the location of polyps and ulcerative colitis ulserosa chronic amoebic.
III.4 Pathology
In macroscopically there are three types of carcinoma of the colon and rectum. Polypoid type or vegetative growth protruding into the lumen of the intestine, cauliflower-shaped and found mainly in the cecum and ascending colon. Type skirus cause constriction resulting in stenosis and obstruction symptoms, mainly found in the descending colon, sigmoid, and rectum. Ulcerative form occurs due to necrosis in the central part contained in the rectum. In advanced stages of colon carcinoma largely ulcerated into malignant ulcers.
Location of colorectal malignancies
III.5 TUMOR CLASSIFICATION
Degree of malignancy carcinoma of the colon and rectum based on histologic malignancy were divided according to Dukes classification. Dukes classification of carcinoma divided by inside infiltration in the intestinal wall.
Classification of carcinoma of the colon and rectum (Dukes)
Figure 2. classification of carcinoma of the sheath
Carcinoma of the colon and rectum began to develop in the mucosa and grows and extends through the wall while the circular oral and aboral direction. In the rectum to the anal spread rarely exceeds two inches. Deployment perkontinuitatum penetrate the surrounding tissue or surrounding organs such as ureter, bladder, uterus, vagina, or prostate. Dissemination occurred to lymph limfogen parailiaka, mesentery, and paraaorta. Penyebarab haematogenous especially to the liver. Peritoneal dissemination mangakibatkan karsinomatosa peritonitis with or without ascites.
The spread of limfogen
III.7 CLINICAL
Clinical symptoms of colon carcinoma in the left in contrast to the right. Left colon carcinomas often are skirotik that cause more stenosis and obstruction, especially because the feces had become solid. On the right colon carcinoma stenosis is rare and still liquid stool so that no obstruction factor
Early signs and symptoms of colorectal carcinoma no. The first symptoms generally arise because of complications, ie bowel physiology interference, obstruction, bleeding, or a result of the spread.
Carcinoma of the left colon and rectum causing bowel habit changes, such as constipation or defecation with tenesmi. The more distal location of the tumor, shrinking feces, or sheep dung, or more fluid with blood or mucus. Tenesmi a symptom commonly found on rectal carcinoma. Acute hemorrhage is rarely experienced. Similarly, pain in the pelvic area of a sign of advanced disease. When the obstruction, the patient feels relieved flatus in the abdomen.
Clinical picture the cecum and ascending colon tumor is not typical. Dyspepsia, general weakness, weight loss, and anemia are common symptoms. Therefore, patients often come in pathetic condition.
Pain in the left colon is more real than the right colon. Place the perceived pain differently because of different embryogenic origin, ie from the middle intestine and colon behind. The pain of the left colon begins below the umbilicus, while the colon kana in the epigastrium.
Factors that determine the symptoms and signs
Clinical features of advanced colorectal carcinoma
III.8 EXAMINATION
Small tumors at an early stage was not palpable on abdominal palpation, when palpable show the state is advanced. Mass in the sigmoid is more obvious than the palpable mass in the colon. Digital rectal examination is mandatory and can be followed by examination rektosigmoidoskopi. Photos of the colon with barium is the completeness of the diagnosis. Biposi done through an endoscope.
III.9 DIAGNOSIS
Based on the established diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma anammesis, pemerikssan physical, digital rectal, and rektosigmoidiskopi or colon with double contrast images. This examination should be performed every three years to the age of 45 years. Certainty of diagnosis berdasrakan anatomic pathology examination.
Additional investigations aimed at the road for a possible urinary stress left ureter, or infiltration into the bladder, and liver and lung for metastasis.
There are several tests in the rectum and colon for the detection of rectal cancer, among them are:
1) complete blood examination, examination of CEA (Carcinoma Embryonic Antigen) test and the faecal occult blood test (FOBT) to see the bleeding on the network
2) Digital rectal examination (DRE) may be used as an initial screening examination.Approximately 75% of rectal carcinomas may be palpable on rectal digital examination will recognize the tumor is located approximately 10 cm from the rectum, the tumor will be felt hard and resound.
Figure 4.Digital rectal examination on Ca sheath
Figure 5.Barium Enema Examination
4) sigmoidoscopy , a procedure to look inside the rectum and sigmoid polyps kakner or whether there are other abnormalities.Tool sigmoidoscope is inserted through the rectum to the sigmoid colon, polyps or tissue samples can be taken for biopsy.Figure 5. sigmoidoscopy
5) Colonoscopy is a procedure to look inside the rectum and sigmoid polyps if there is cancer or other abnormalities.Tool colonoscope is inserted through the rectum to the sigmoid colon, polyps or tissue samples can be taken for biopsy.Figure 6.Colonoscopy
If a tumor is found from one of the above examination, biopsy should be performed.In anatomic pathology, adenocarcinoma is the most common type which is about 90 to 95% of colon cancer. Other types are squamous cell carcinomas, carcinoid tumors, adenosquamous carcinomas, and undifferentiated tumors.When the diagnosis of rectal cancer has been ascertained, then performed a procedure to determine tumor stage. These include a computed tomography scan ( CT scan ) of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis, complete blood count (CBC), hepatic and renal function tests, urinanalysis, and measurement of tumor marker CEA (carcinoembryonic antigen).
Definite diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma
Summary of diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma
iii. 10 The differential diagnosis
Various abnormalities in the abdominal cavity is the same or similar symptoms of colorectal carcinoma is a peptic ulcer, gastric neoplasms, cholecystitis, liver abscess, liver neoplasm, appendix abscess, mass periapendikuler, amuboma, diverticulitis, colitis ulserosa, enteritis regionalist, post-radiation proctitis and polyps rectum.
The differential diagnosis
III.11 complications
Obstruction
Left colonic obstruction is often the first sign of colon carcinoma. Colon can be very large, especially the cecum and ascending colon. Obstructive type is called type dileptik.
Perforation
Perforation occurred in the vicinity of the tumor due to necrosis and obstruction of mnyebabkan accelerated by the pressure inside the colon cavities increasingly rising. Common cause of perforation peritonitis is usually accompanied by symptoms of sepsis. Perforation have been fatal if not promptly rescued. Sometimes there is perforation with abscess formation around the tumor in response to the peritoneum. Peritoneum and the surrounding tissues surrounding the perforation so that contamination is limited and formed an abscess. Tumors located near the stomach can lead to fistula gastrokolika with symptoms of nausea and vomiting fecal. Tumors located near the bladder can lead to fistula vesikokolika pneumaturia sign.
III.12 Governance
The only possibility of curative therapy is surgical act. The main purpose is to facilitate acts of gastrointestinal surgery, either curative or nonkuratif. Palliative chemotherapy and radiation and did not gave the benefit of therapy.
Followup consisted of surgical resection of primary carcinoma of the area and regional lymph nodes. When there is distant metastasis of primary tumopr also be resected with the intention of preventing obstruction, bleeding, anemia, urinary incontinence, fistula, and pain.
Rectal carcinoma, surgical technique chosen depends on the location, particularly within the lower bound and anal carcinoma. As far as possible the internal anal sphincter to be preserved to avoid preternaturalis.
Curative Surgery performed when no symptoms are found both local and distant spread. In the cecum or ascending colon tumor hemikolektomi done right, then end to end anastomosis. In the tumor in the hepatic flexure done well hemikolektomi. In the transverse colon tumor resection transverse colon, and end to end anastomosis while in the descending colon tumors do hemikolektomi left.Sigmoid resection in tumors and in tumor rectal sigmoid sepertigga proximal anterior resection. In the middle third rectal tumor resection to preserve the anal sphincter, whereas the third tumor distal amputations performed abdominoperineal resection of the rectum through Quenu-Miles. In this operation the anus also excluded.
A palpable tumor on digital rectal diamggap generally too low for anal sphincter preservation action. Only in the early stages of tumor local excision can be accounted for by retaining anus.
At surgery, Miles abdominoperineal menuryut Quenu, rectum and sigmoid with mesosigmoid released, including the lymph nodes and retroperitoneal pararektum. Then through a perineal anus insis completely excised and removed through the abdomen to the rectum.
Low anterior resection of the rectum is done through laparotomy by using a stapler to make colorectal anastomosis or low koloanal.
Local excision can be performed through the Kars rektoskop inoma limited.Pender ita selection must be done carefully, such as by using endoscopy to determine the level pentebaran ultrasonografik inside wall of the rectum and the presence of malignant lymph pararektal.
Another way that can be used for specific indications and the selection is fulgerasi (electric coagulation). On this way can not be performed histopathological examination. This method is sometimes used in patients at high risk for surgery.
Coagulation with a laser is used as palliative therapy. While radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy used as adjuvant therapy. Follow that preceded and followed by a surgical fire radioter called sandwich therapy.All of them sometimes have a positive effect for a limited time.
Complications that often occur in the radical abdominoperineal resection of the rectum and lower anterior resection of the rectum is impaired fungsis sex. On dissection of the lymph nodes and p ararektal around promonterium and retroperitoneal regions in the (pre) aortal performed excision of the autonomic nervous too, sympathetic and parasympathetic. Sexual disorders may be less or lost libido, impotence, gaangguan vaginal lubrication, orgasm or ejaculation. Disturbance may be one of several combinations of the above-mentioned disorders. With a special surgical techniques that smooth and precise incidence of these complications can be reduced.
Figure 7. Resection and anastomosis
Palliative Medicine
Palliative resection of the tumor is done to prevent or menagatsi mengehentikan obstruction or bleeding that patient quality of life better. If the tumor can not be diangakat, or bypass surgery can be performed preternaturalis anus. In the liver metastasis is not more than two or three can be considered excision of metastatic nodules. Giving cytostatic through a.hepatika, namely the selective perfusion, sometimes longer with embolization therapy, can successfully malignant cell growth inhibition.
Prognosis
Prognosis depends on the presence or absence of distant metastases, the spread of tumor classification and rate of tumor cell malignancy.
For tumors confined to the intestinal wall without the spread, the five-year survival rate was 80%, which pass through walls without the deployment of 75%, with the spread of the gland 32%, and with a p Ersen distant metastases.When accompanied by poor tumor cell differentiation, prognosis is very poor.
III.13 colostomy
Colostomy is also called the anus kolokutaneostomi preternaturalis made for temporary or persistent. Temporary colostomy is created, for example in patients with acute abdomen with peritonitis who had done some of colonic resection. In the circumstances, the burden of new tomosis Anas stool passage is an act that can not be accounted for.Therefore, for securing the anastomosis, fecal stream diverted through a temporary colostomy stoma is usually referred to two double-barrel stroma. Hartmann manner, making the anastomosis was postponed until the inflammation in the stomach have been there.
Permanent colostomy is created on rektoanal abdominoperineal resection according to Miles in the form of anal-Quenu preteranaturalis true.Esofagostomi, gastrostomi, yeyunustomi, and sekostomi usually a temporary stoma. Ileostomy and colostomy is often a permanent stoma.
Decompression colostomy is an indication of intestinal obstruction, a temporary stoma for bowel resection surgery on inflammation, or perforation, and the anus after bowel resection distal to protect the distal anastomosis. Colostomy stoma may be Kalt (kolostoma loop) or end stoma (end kolostoma).
At kolostoma sigmoid bowel habit usually the same as the original. Many people hold a rinse once a day so they are not bothered by the spending of stomanya stool. Kolostoma the transverse colon removing intestinal contents several times a day because of the contents of the transverse colon is not solid, so it is more easily managed.
Preternaturalis rectum often cause complications. Parastoma hernia may contain colon, omentum, or intestine that often occurs in obese people. Prolapse, stenosis, necrosis, and retraction is a complication is less than perfect technique. Infection of the abdominal wall and skin irritation sometimes occurs frequently seen due to the rest of the digestive stimulation.
Entrostoma therapy is an expert who served specifically to treat and membimbingpenderiata and anus with his family to confront preternaturalis.
Figure 8. Resection and colostomy
The types of colonstomy based on its location:
SECTION IV
CONCLUSIONS
The incidence of carcinoma of the colon and rektun in Indonesia is quite high, as well as mortality.Incidence in men comparable with women. About 75% are found in rektosigmoid. Digital rectal examination is a determinant of rectal carcinoma.
Risk factor for carcinoma of the rectum is the degeneration of colonic polyps, genetic factors, lack of eating fibrous foods such as vegetables and bsayur fruits, and high consumption of animal fats.
In macroscopically there are three types of carcinoma of the colon and rectum, the polypoid type or vegetative type skirus, ulcerative type.In advanced stages of colon carcinoma largely ulcerated into malignant ulcers.
Degree of malignancy carcinoma of the colon and rectum based on histologic malignancy were divided according to Dukes classification of carcinoma infiltration by them in the intestinal wall.The spread of carcinoma of the colon and rectum are haematogenous, limfogen and perkontinuitatum.
Clinical symptoms of colon carcinoma in the left in contrast to the right. Carcinoma of the left Koon cause more stenosis and obstruction. On the right colon carcinoma stenosis is rare and still liquid stool so that no obstruction factor. The first symptoms generally arise because of complications, ie bowel physiology interference, obstruction, bleeding, or a result of the spread. Carcinoma of the left colon and rectum causes changes in bowel habit. Acute hemorrhage is rarely experienced. Pain in the left colon is more real than the right colon. Place the perceived pain differently because of different embryogenic origin, ie from the middle intestine and colon behind. The pain of the left colon begins below the umbilicus, while from the right colon in the epigastrium.
Based on the established diagnosis of colorectal carcinoma anammesis, pemerikssan physical, digital rectal, and rektosigmoidiskopi or colon with double contrast images. Complications that can occur in colorectal carcinoma is obstrukis and perforation.
Therapy consisted of curative and palliative therapy. Curative therapy is surgery n premises.Palliative therapy with chemotherapy and radiation.
REFERENCES
1. Sabiston, David C. Buku Ajar Bedah Bagian 2. Penerbit Buku Kedokteran EGC. Jakarta. 1994. Hal: 14-18, 36-42.
2. Sjamsuhidajat. R, Wim de Jong. Buku Ajar Ilmu Bedah Edisi 2. Penerbit Buku Kedokteran. EGC. Jakarta. 2005. Hal: 658-667
3. Schwartz. Intisari Prinsip-prinsip Ilmu Bedah Edisi 6. Penerbit Buku Kedokteran EGC. Karta. 2000. Hal:
4. Doherty GM. Current Surgical Diagnosis and Treatment. USA : McGraw Hill. 2006. Hal: 658-668.
5. http://id.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kanker_kolon_dan_rektum.
6. http://medlinux.blogspot.com/2009/01/karsinoma-rektal.html.






















No comments:
Post a Comment